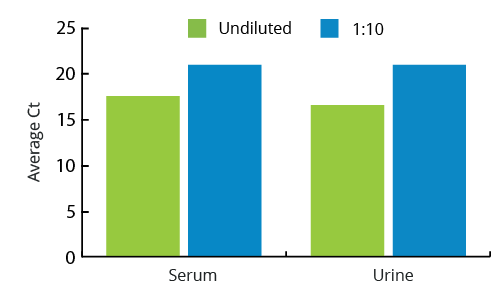
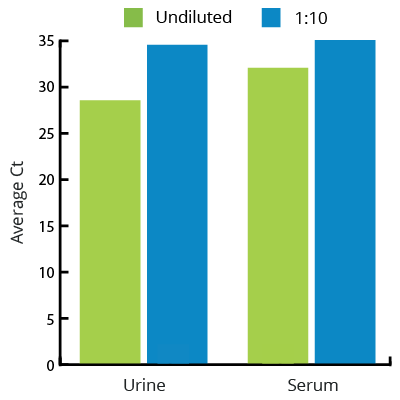
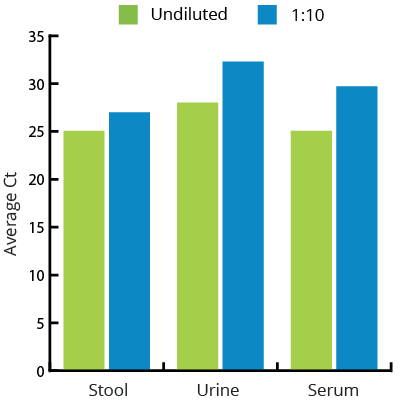
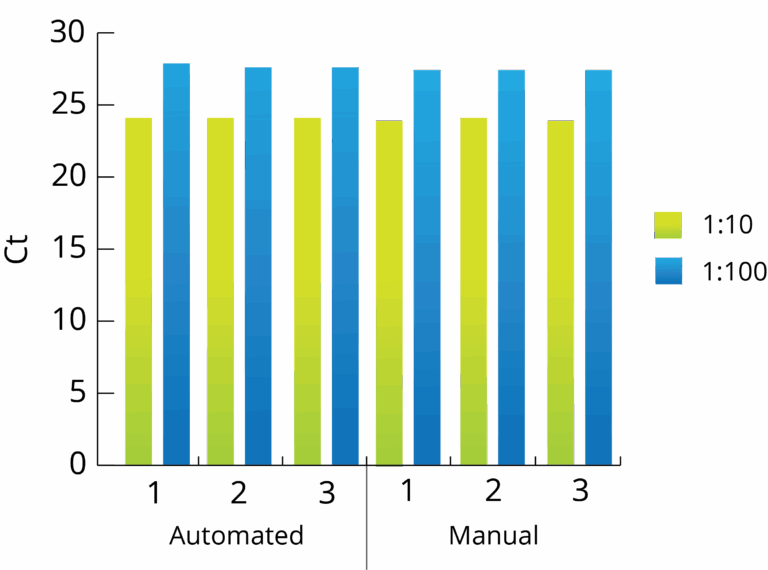
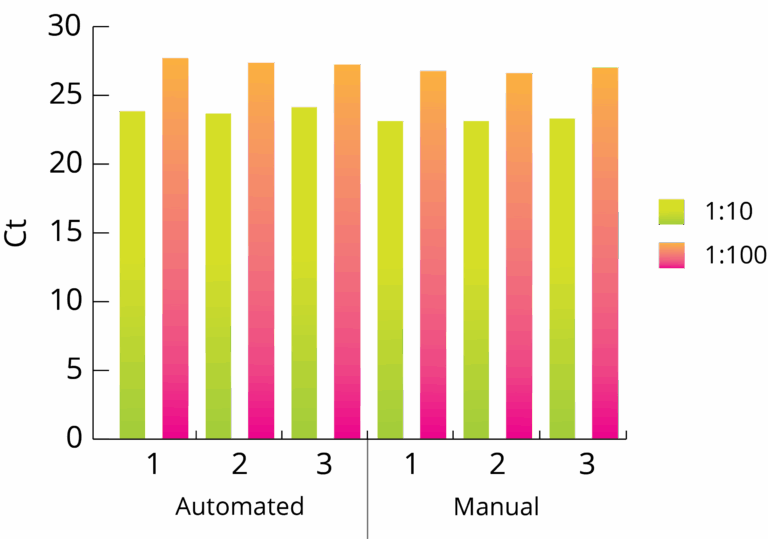
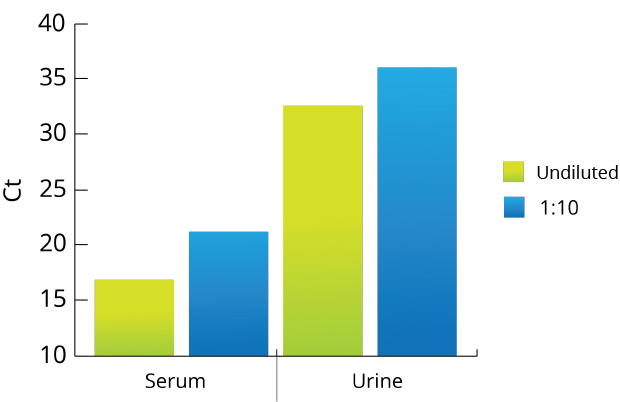
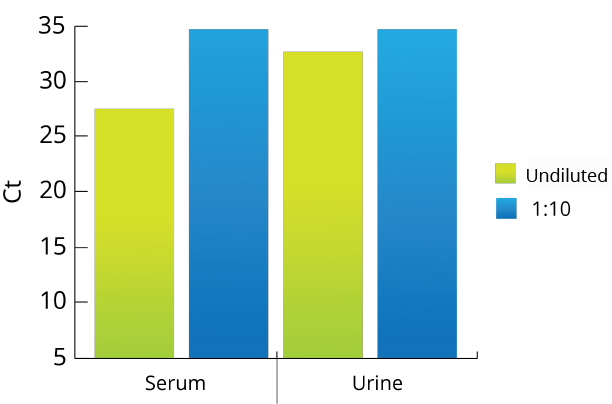
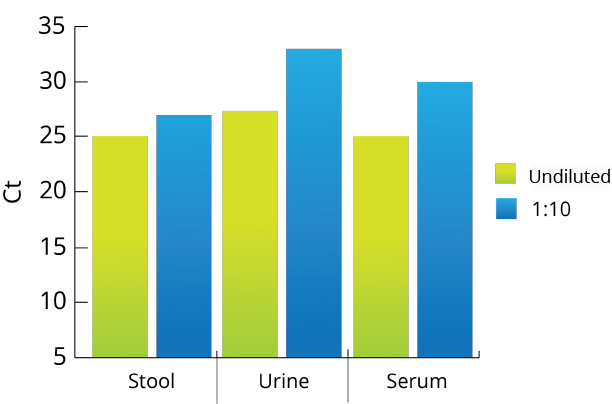
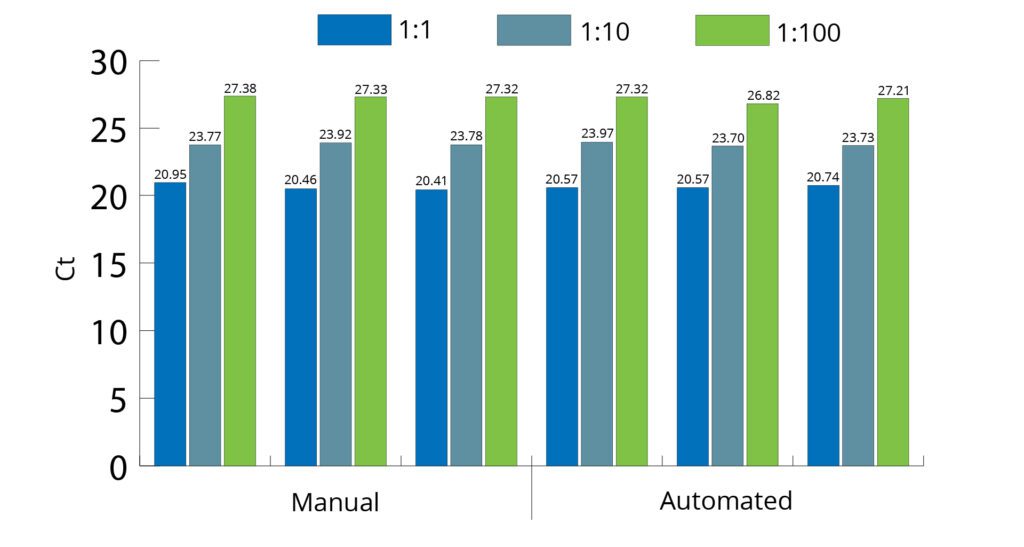
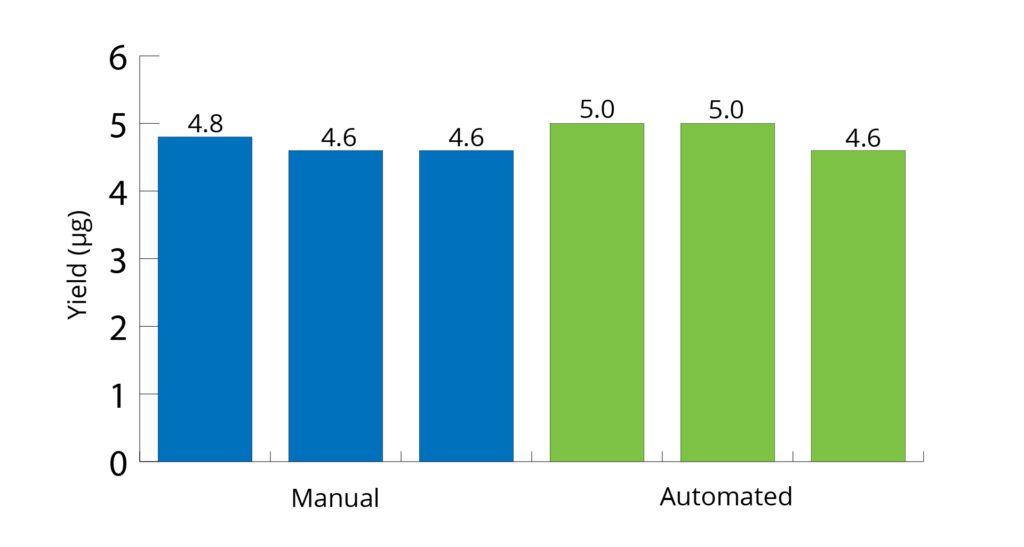
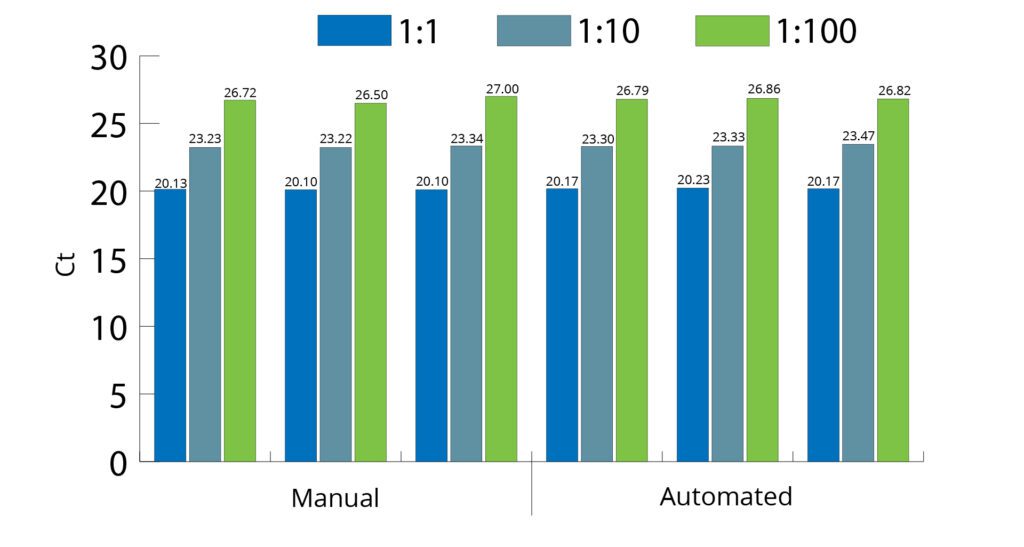
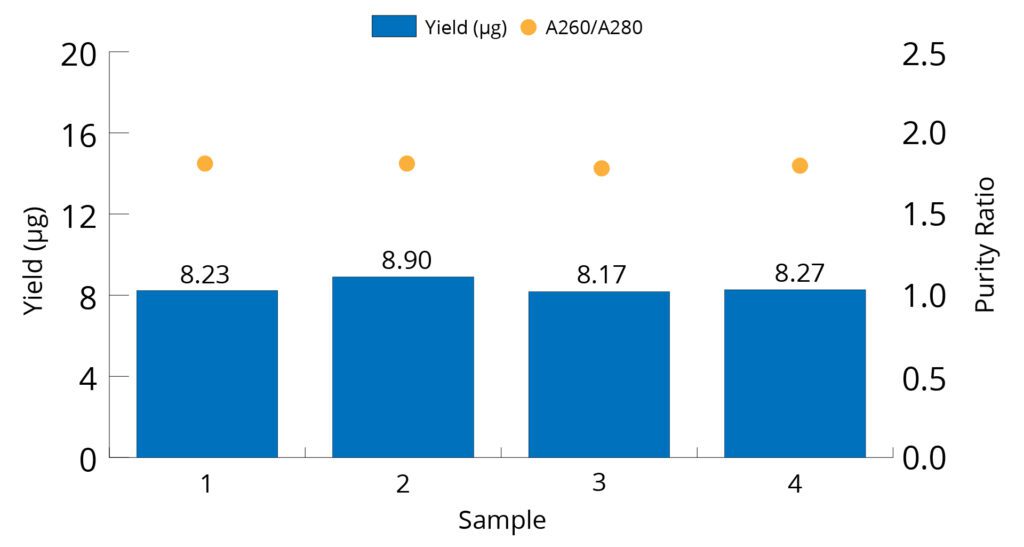
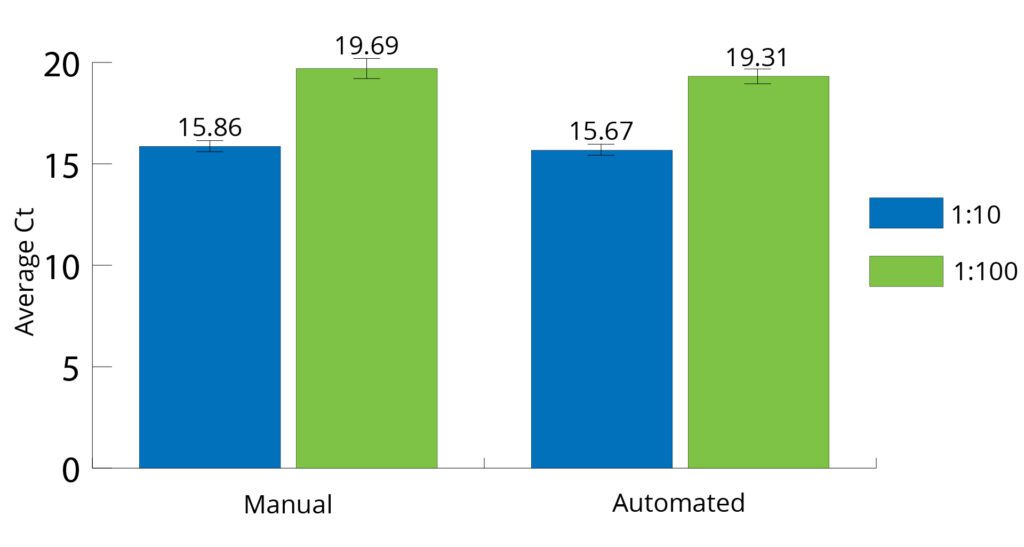
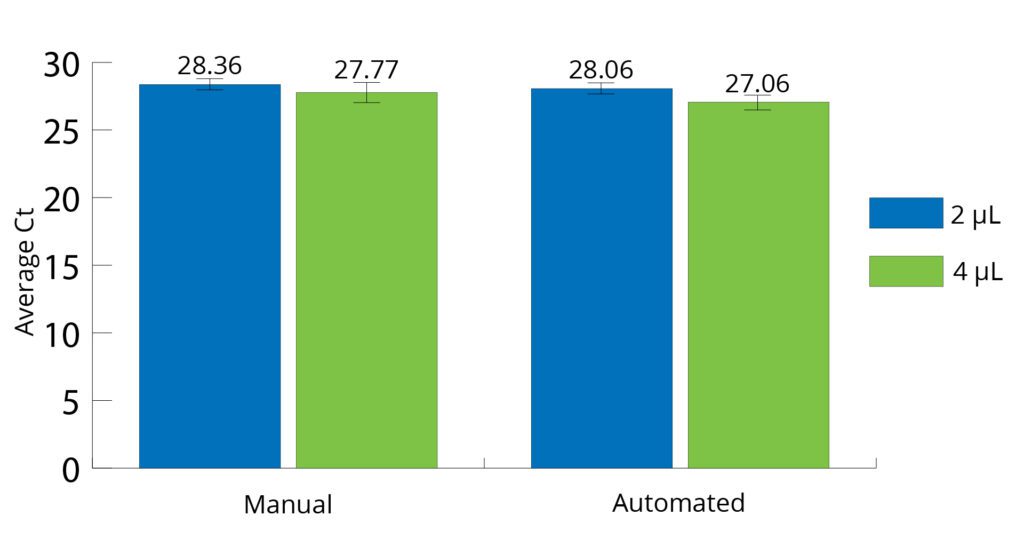
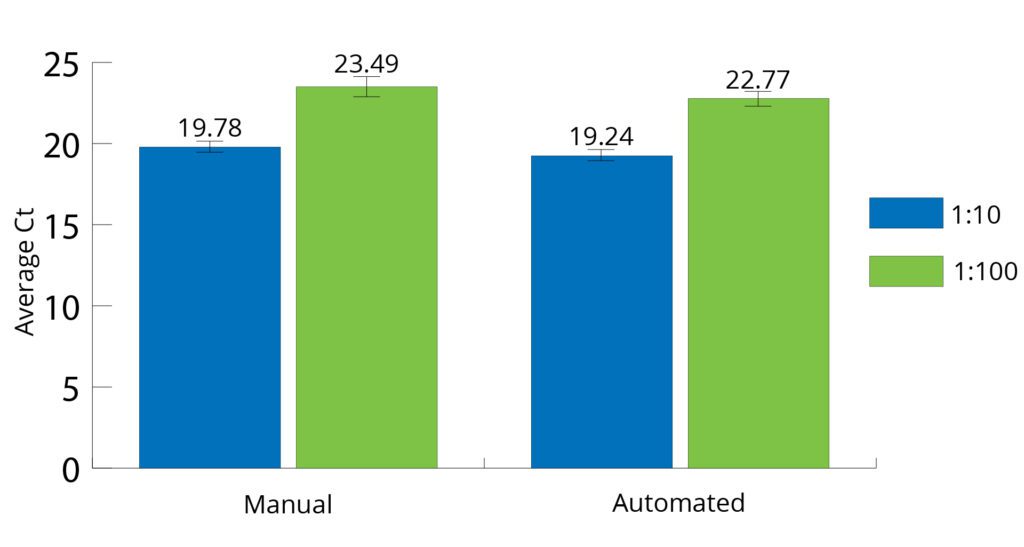
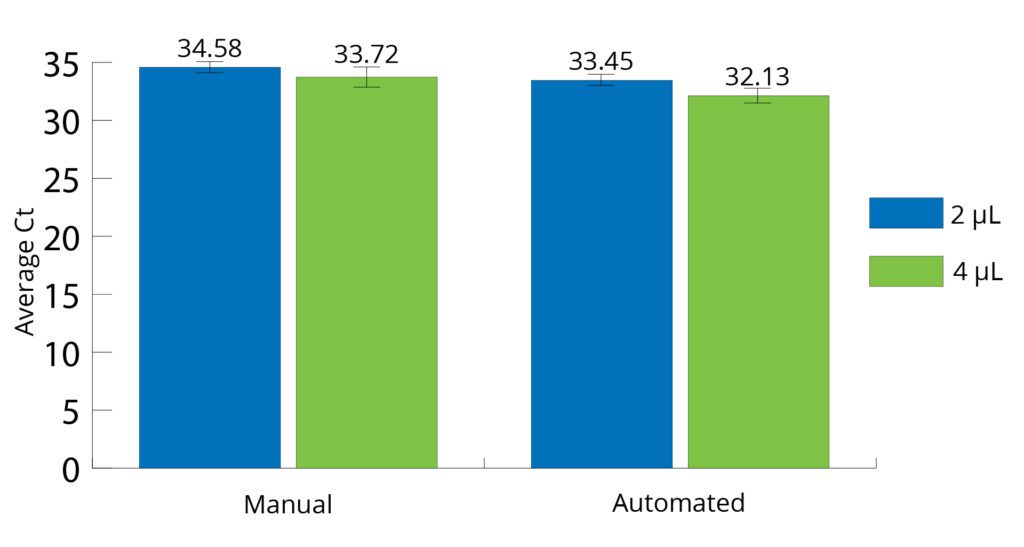
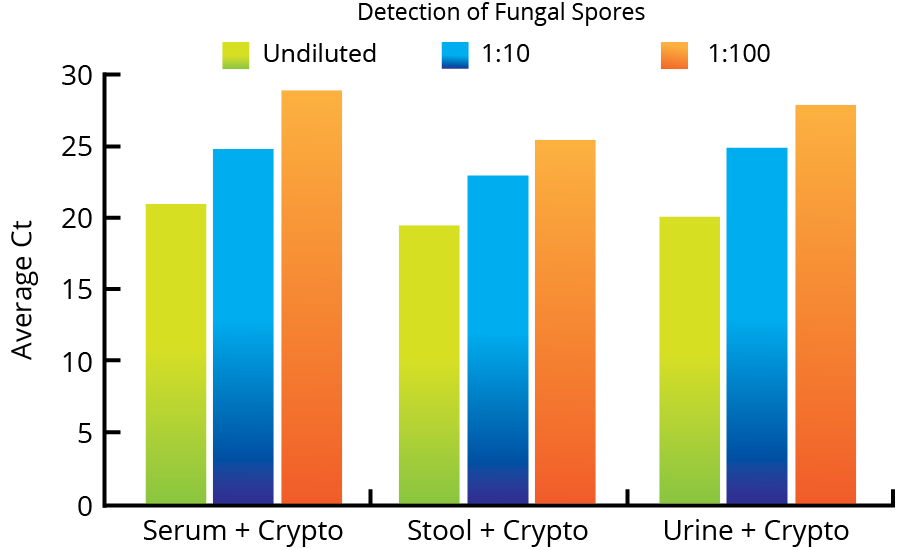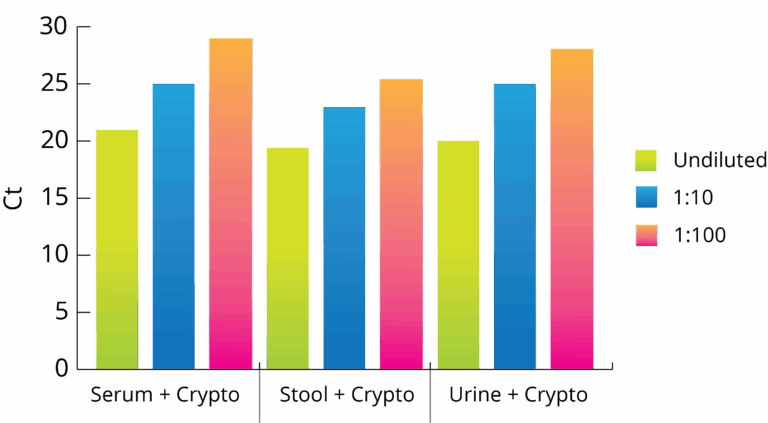All Mag-Bind® kits can be automated on most programmable robotic platforms, liquid handlers or magnetic processors. Learn more.
Off-the-shelf product doesn’t suit your needs? We’ll work with you to develop a customized product. Learn more.
Dedicated applications support will consult with you to develop and implement an automated solution that fits your specifications. Learn more.