Kiranmai Durvasula¹, Carisa Townsend¹, Julie Baggs¹, and Travis Butts¹
¹Omega Bio-tek, Inc, Norcross, GA 30071
Introduction
Plasmids play a crucial role in the manufacturing and development of mRNA-based vaccines and therapeutics. As essential tools in molecular biology, plasmids serve as templates for in vitro transcription (IVT) processes, enabling the production of high-quality mRNA molecules for further use in the formulation of vaccines and therapeutic agents.
The mRNA production workflow consists of several steps and the fine-tuning of each step — from plasmid template quality to post-transcription purification — is essential for maximizing yield and integrity. High-quality, endotoxin-free plasmid DNA is foundational to this workflow by promoting efficient transcription, consistent mRNA integrity, and regulatory acceptance. Post-transcription purification steps which remove IVT by-products, enzymes, nucleotides, and other impurities are critical for ensuring the efficacy and safety of mRNA-based therapeutics.
Learn more about the Mag-Bind® Endo-free Plasmid Midi Kit automated on the MagBinder® Fit24.
Automation and scalability are essential factors in advancing high-throughput screening processes, particularly during the early discovery phase of mRNA-based therapeutics. Integrating automation into laboratory workflows allows researchers to process a larger number of samples efficiently and consistently. Moreover, scalable methods support the growing demand for rapid screening of numerous plasmid constructs, streamlining the identification of promising candidates for further development. By embracing both automation and scalability, laboratories can significantly enhance their capability to discover and develop new mRNA-based therapeutics at an accelerated pace.
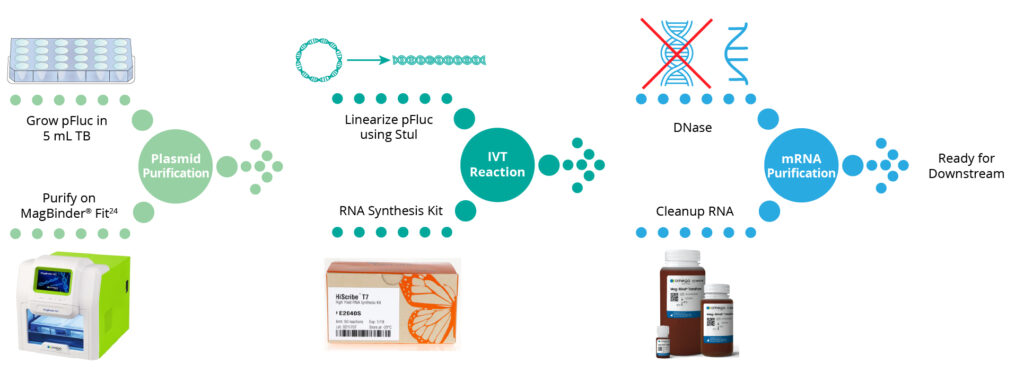
In this application note, we provide a proof-of concept workflow (Figure 1) from automated purification of endotoxin-free plasmid DNA using Omega Bio-tek’s Mag-Bind® Endo-free Plasmid Midi Kit (M1272) to employing Mag-Bind® TotalPure NGS (M1378) to remove contaminants from the IVT reaction. These kits follow a magnetic bead-based approach and can be automated on most open-ended automation platforms such as Hamilton Microlab® STAR™, Thermo Fisher Scientific’s KingFisher® system, Dynamic Devices’ Lynx®, as well as Omega Bio-tek’s MagBinder® Fit24.
mRNA Production Workflow
Materials & Methods
Plasmid Growth and Purification
1 ng of NEB’s FLuc Control template was transformed into E. coli strain DH5α and plated in the presence of ampicillin antibiotic. A single colony from this plate was isolated and inoculated into 5 mL of Terrific Broth (TB) culture, supplemented with 100 μg/mL of ampicillin in a 24-well plate. The plate was incubated at 37 °C with shaking at 385 rpm. After an overnight culture, NEB’s FLuc Control plasmid from this 5 mL culture was purified using the Mag-Bind® Endo-free Plasmid Midi Kit automated on the MagBinder® Fit24 platform, following manufacturer’s instructions. The upfront alkaline lysis and lysate clearance were carried out offline. The lysate is transferred to a 5 mL MB Fit24™ reagent cartridge (PB07-5-200), and subsequent bind-wash-elute steps were performed on the MagBinder® Fit24 with a protocol run time of ~ 70 min for up to 24 samples. Purified plasmid DNA was eluted in 100 μL volume and quantified using Thermo Scientific’s NanoDrop™ 2000c system, and endoxin levels were determined using Charles River’s Nexgen-PTS device using their Endosafe® LAL Cartridge (1 – 0.01 EU/mL). 100 ng of purified plasmid DNA was run on 1% agarose gel to assess its integrity and ImageJ densitometry was employed to estimate the percentage of supercoiled plasmid DNA in the total plasmid DNA that was purified.
IVT Transcription
Purified plasmid was linearized with StuI restriction digestion enzyme. Post-linearization, the plasmid was run on an agarose gel to visualize plasmid digestion. 1 μg of linearized pFLuc was used in a 20 μL IVT reaction using NEB’s HiScribe® T7 High Yield RNA Synthesis Kit following manufacturer’s protocol. DNase I step was included to remove the template DNA.
mRNA Purification
After transcription, synthesized mRNA was cleaned up using Mag-Bind® TotalPure NGS (M1378) at a ratio of 1.2X to remove the unwanted contaminants from the IVT reaction. Post cleanup, RNA was quantified using Thermo Scientific’s NanoDrop™ 2000c system. RNA was also analyzed on TapeStation for size and integrity of RNA that was synthesized.
The end-to-end workflow from plasmid purification to IVT transcription to mRNA purification is depicted in Figure 1.
Results and Discussion
Yield and purity of purified plasmid DNA (pFLuc) was measured using spectrophotometry, the values of which are shown below in Table 1. The yield ranged between 40 to 44 μg from a 5 mL culture input with excellent purity ratios of A260/A280 = ~1.8 and A260/A230 = ~2.3. The purified plasmids had endotoxin levels < 0.04 EU/μg as assayed on Charles River’s Nexgen-PTS device. Readings < 0.1 EU/μg are generally considered endotoxin-free and these results validate that the purified plasmids are endotoxin-free and suitable for highly sensitive downstream applications such as primary cell transfection, in vivo studies, gene therapy and vaccine research.
Table 1. Plasmid Yield, Quality, and Endotoxin Levels extracted using the Mag-Bind® Endo-free Plasmid Midi Kit
| Plasmid | Yield (µg) | A260/A280 | A260/A230 | Average Endotoxin Levels |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pFluc purified from 5 mL TB culture | 40.7 | 1.85 | 2.3 | < 0.04 EU/µg |
| 44.1 | 1.85 | 2.3 | ||
| 43.6 | 1.85 | 2.3 |
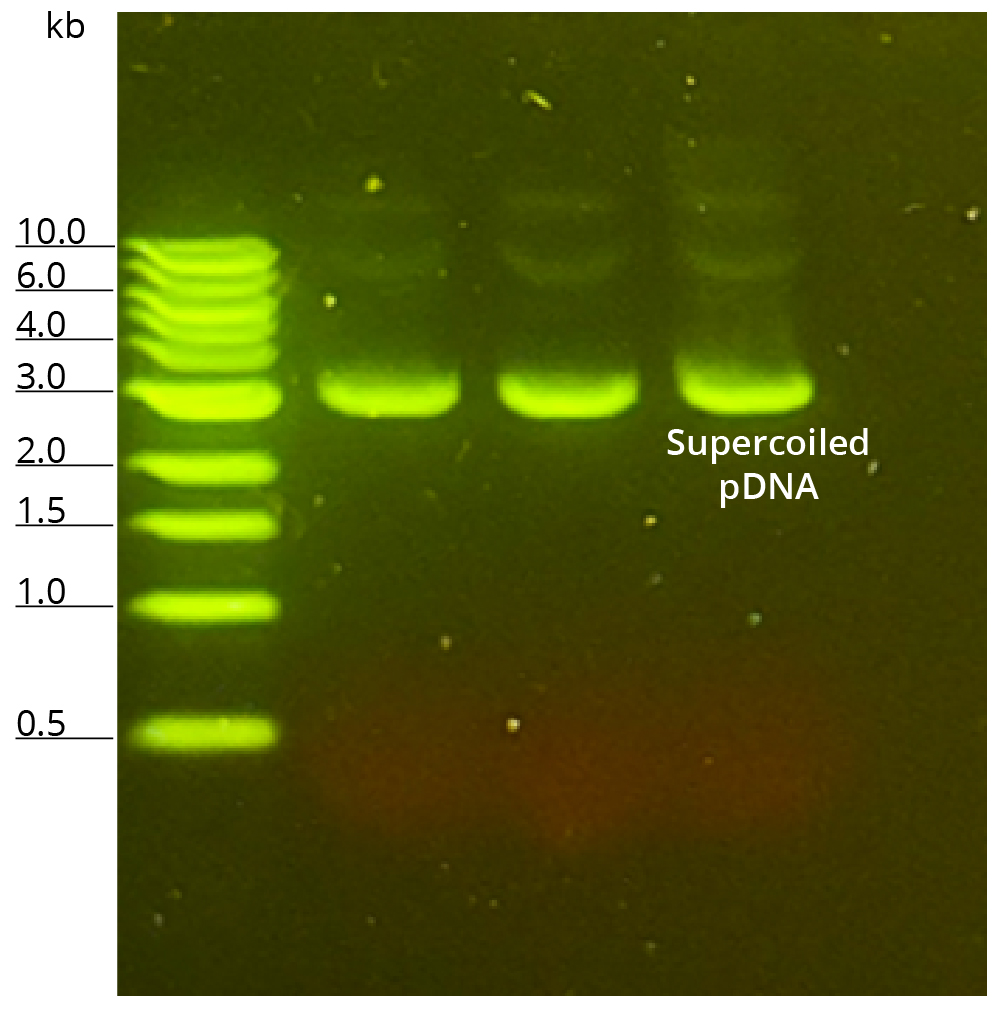
Plasmid integrity was ascertained by running 100 ng of purified pFLuc on 1% agarose gel (Figure 2). Plasmid ran as a single well-defined band, primarily in supercoiled conformation. Based on the ladder, plasmid size was estimated between 3 and 4 kb which agrees with the published pFLuc size of 3925 bp. The agarose gel image was further analyzed using ImageJ densitometry to estimate the percentage of supercoiled conformation on the gel. ImageJ densitometry software analyzes the bands in a particular lane and calculates the percentage of supercoiled DNA by comparing its intensity to the total intensity of all plasmid forms in that lane. This analysis estimates supercoiled plasmid conformation to be ~90.2%. Supercoiled plasmid DNA serves as the precursor for linear DNA templates, and ensuring the supercoiled DNA percentage is within the defined parameters is critical to achieving effective production of linear DNA templates and subsequent mRNA production. Guidance for Industry: Considerations for Plasmid DNA Vaccines for Infectious Disease Indications¹ by the US Food and Drug Administration recommends a minimum specification for supercoiled plasmid content (preferably >80%) to control the plasmid quality for early-phase studies. With > 90% supercoiled plasmid purified using Mag-Bind® Endo-free Plasmid Midi Kit, this kit satisfies the FDA specification and establishes itself to be a great candidate for early-phase workflows.
Supercoiled Plasmid DNA
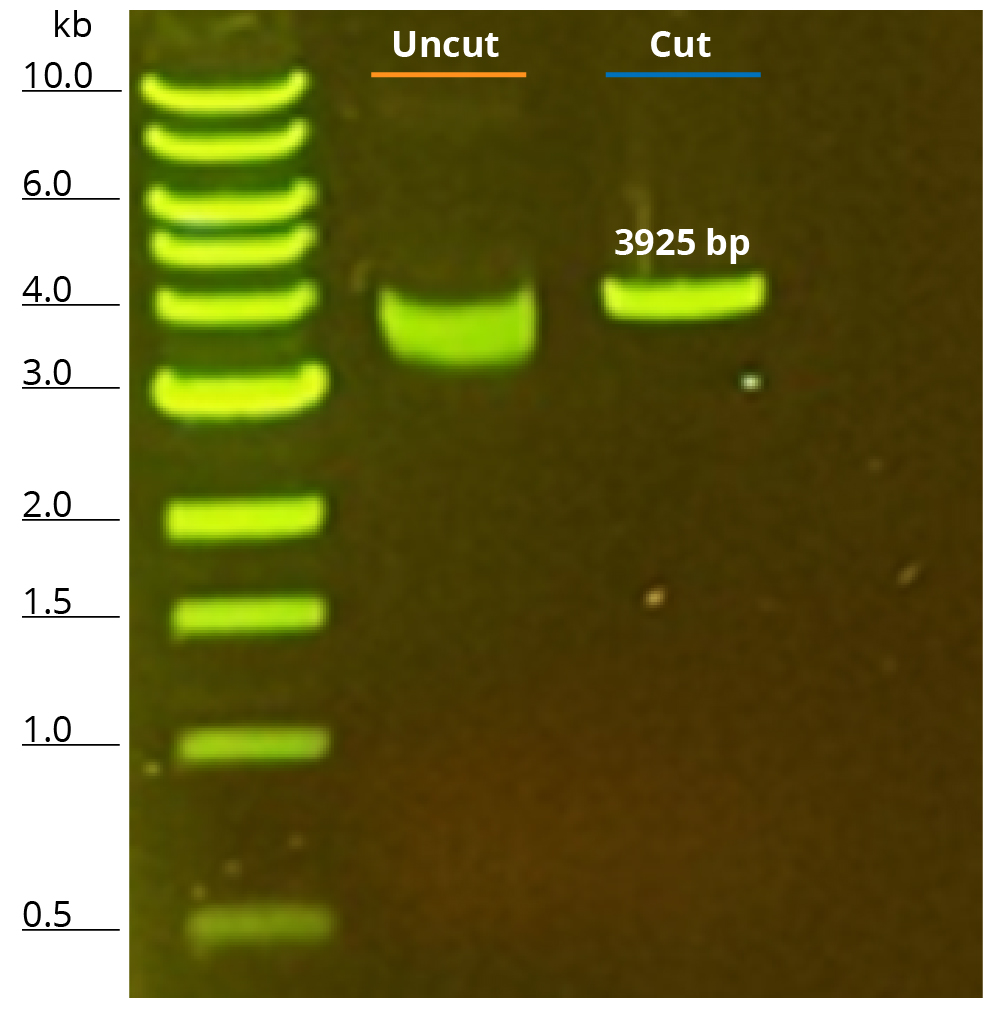
Restriction Enzyme Linearization
High Integrity RNA
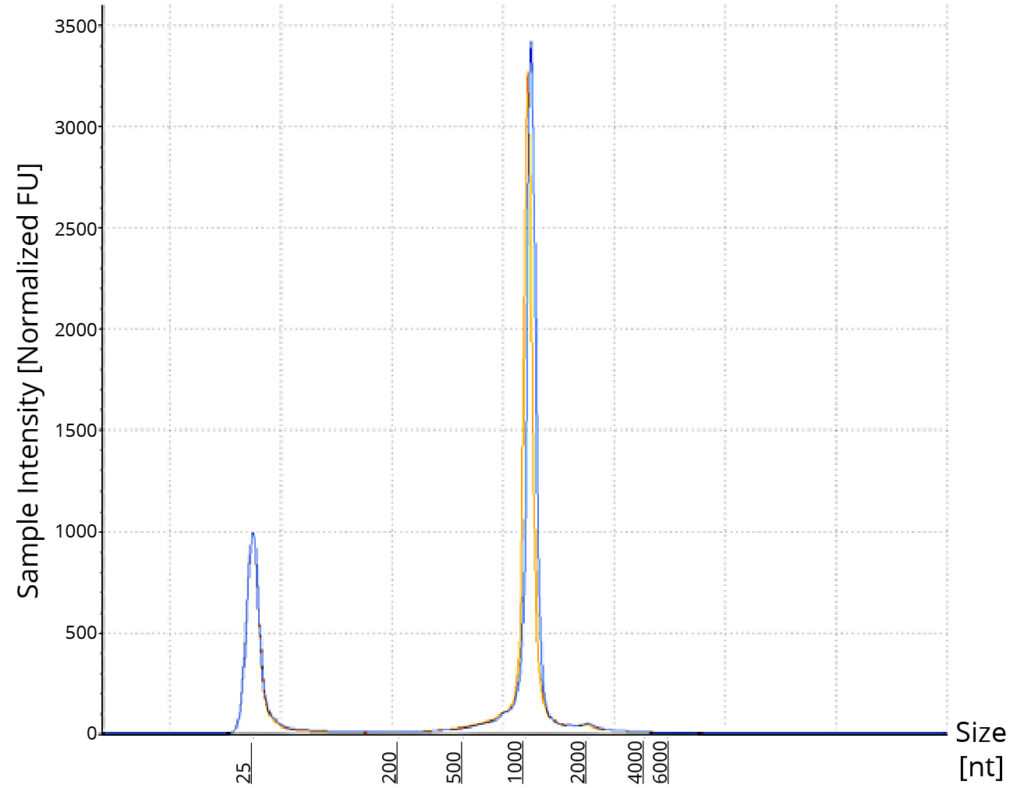
Purified pFLuc was linearized using StuI restriction enzyme. 100 ng of linearize plasmid along with its uncut control was run on 1% agarose gel (Figure 3). The electrophoresis image shows a single well-defined band post restriction digestion, closer to the 4 kb marker, agreeing with published sizing of pFLuc at 3925 bp. The uncut plasmid on the gel appears to run faster than its linear counterpart which also aligns with the fact the uncut is primarily supercoiled and the compact, twisted shape of the supercoiled plasmid helps navigate through the gel faster than its linear counterpart. Upon confirmation of linearization, 1 μg of linearized pFLuc was used in a 20 μL IVT reaction using NEB’s HiScribe® T7 High Yield RNA Synthesis Kit following manufacturer’s protocol to synthesize mRNA. A DNase I step was included to remove any contaminating, unused template DNA. Post-transcription cleanup was performed using Omega Bio-tek’s Mag-Bind TotalPure® NGS using a bead-to-sample ratio of 1.2X. This cleanup was performed to eliminate DNase, enzymes, nucleotides, and other unwanted impurities from the synthesized mRNA. The yield of the synthesized RNA was found to be ~ 152 μg as quantified using spectrophotometry and in line with the expected yield of ~180 μg using 1 μg of control templates. A260/A280 and A260/A230 ratios were >2.0 corroborating the high purity of synthesized RNA. The TapeStation analysis also supports the high quality and integrity of the eluted RNA as shown in Figure 4.
Conclusions
The integration of high-quality, endotoxin-free plasmid DNA purification and post-transcription purification methods is pivotal for the successful production of mRNA-based vaccines and therapeutics. By utilizing automated, scalable workflows such as those enabled by Omega Bio-tek’s Mag-Bind® kits and compatible automation platforms, laboratories can ensure consistent mRNA yield and integrity while meeting the demands of high-throughput screening. This streamlined approach not only enhances the efficiency and reproducibility of the mRNA production process but also supports rapid discovery and development of promising therapeutic candidates, ultimately accelerating innovation in the field of mRNA-based medicine.
References
1. Guidance for Industry: Considerations for Plasmid DNA Vaccines for Infectious Disease Indications. U.S. Food and Drug Administration, 2007. https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/considerations-plasmid-dna-vaccines-infectious-disease-indications
SL-0161
Related Products
-
Bacterial Plasmid
Mag-Bind® Endo-free Plasmid Midi Kit
$0.00 – $1,032.60Price range: $0.00 through $1,032.60 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
Cleanup
Mag-Bind® TotalPure NGS
$0.00 – $4,481.70Price range: $0.00 through $4,481.70 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page